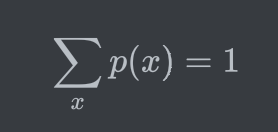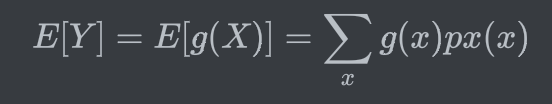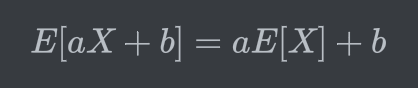Random Variables (1)
Random Variable (1)
현재 정리하는 내용은 KAIST EE의 이융 교수님, Probability and Intorductory Random Process 강의를 참고하여 작성했습니다.
Random variable : Idea and Formal definition
-
현실에서 많은 random variable들은 숫자 형태로 존재한다.
→ e.g., stock price -
또한, 숫자 형태가 아닌 것들에 숫자를 부여함으로써 수학적 편리함을 갖게 하기도 한다.
→ e.g., ‘0’ for male and ‘1’ for female.
→ 이전에 봤던 two rolls of tetrahedral dice의 예제를 보자.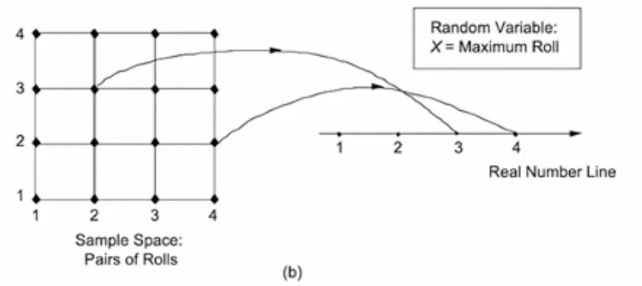
→ (면의 번호, 면호 번호)로 주어진 sample space 상의 random variable에 숫자를 부여하는 모습이다. -
그렇다면, 이제 random variable의 정의를 확인해보자.
→ Mathematically, a random variable X is a function which maps from Ω to R. (R : Real Number)
→ Notation : Random variable X, numerical value x.
→ 물론, 동일한 sample space에서 다른 random variable(X)를 만들 수 있다.
→ For a fixed value x, we can associate an event that a random variable X has the value x, i.e., {w ∈ Ω | X(w) = x}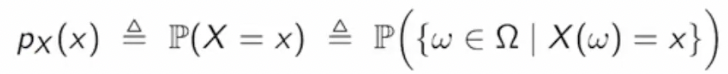
→ For a discrete random variable X, we call px(x) probability mass function (PMF)
→ PMF는 이산 확률 변수에서 특정 값에 대한 확률을 나타내는 함수이다!
-
그러면, notation에 대한 예제를 살펴보자!
-
주사위를 굴렸을 때, sample space Ω = {1,2,3,4,5,6}이다.
-
Random variables X의 대한 정의를 내려보자. 얘는 함수다!
X = 1 for even numbers.
X = 0 for odd numbers.
-
그럼 이 놈에 대한 Notation은 다음과 같이 된다.
Event A1 = {w ∈ Ω | X(w) = 1} = {2, 4, 6} ⊂ Ω
→ simply, A1 = { X = 1 }Event A2 = {w ∈ Ω | X(w) = 0} = {1, 3, 5} ⊂ Ω
→ simply, A2 = { X = 0 } -
A1 = { X = 1 }이 A1 = {w ∈ Ω | X(w) = 1} 이렇게 표현됨 또한 알아야 한다.
-
그리고 random variable X는 함수이다. which maps from Ω to R
X x P(X=x) 확률 변수 X
Sample space 내에 있는 각 원소에
하나의 실수값을 대응시키는 함수X가 할당하는 실수 값 실수 값이 나올 확률 값
PMF
-
Popular discrete random variables
-
Only binary values.
→ p ∈ [0, 1]X = 0, w.p. 1-p,
X = 1, w.p. p
w.p. : with probability
- In other words, px(0) = 1-p, px(1) = p from our PMF notation.
→ success/failure, head/tail - Very useful for an indicator rv(random variable) of a event A.
- In other words, px(0) = 1-p, px(1) = p from our PMF notation.
-
Uniform X with paramete a, b (integer a,b, where a <= b)
-
그렇다면, Ω = {a, a+1, …, b}가 될 것이고, 여기서 uniformly at random하게 숫자를 뽑는다고 해보자.
-
그럼 X에 대해 몰라도 괜찮다! → 모든 숫자가 동일한 확률을 갖게 되니까
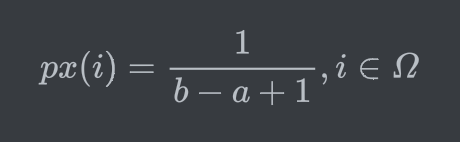
typora로 수식 쓰는 법을 알아냈다.
-
-
Binomial X with parameter n, p
→ Models the number of success in a given number of independent trials.-
n번의 동전 던지기를 하고, p의 확률로 앞면(success)이 나온다고 하자. 그럼 여기서, k번의 앞면이 나올 확률을 어떻게 구할까?
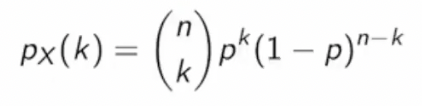
→ 요렇게 나오게 된다!
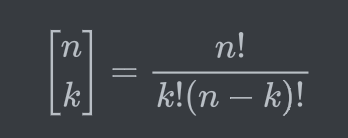
→ 괄호 표시가 다른건 내가 익숙하지 않아서다.
-
-
Gemetric X with parameter p
- 무한히 많은 independent한 시도 끝에(k번의 시도) 성공하는 확률
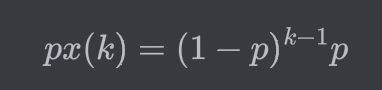
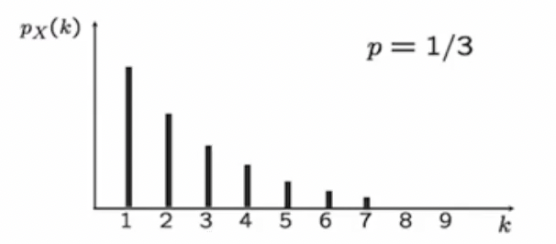
- 그림처럼 모델이 성공을 할 때까지 기다리는 양상을 보인다.
Summarizing random variables : Expectation and Variance
-
Expectation(기대값)의 표현 :
-
Expectation은 RV에 대한 평균이라고 볼 수 있고, 흔히 아는 산술 평균이 아닌 확률 평균이다.
-
확률 평균 : 각각의 변수의 확률을 고려한 평균
-
수식 표현
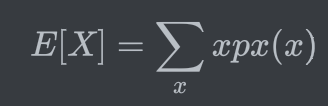
→ 각각의 변수의 확률을 고려했다고 했으니까, </br>
→ px(x) : relative frequency of value x
-
-
Properties of Expectation
- if X >= 0, E[X] >= 0
- if a <= X <= b, a <= E[X] <= b
- For a constant c, E[c] = c
-
For a rv X, Y = g(X) is also rv.
→ 앞서 말한 것 처럼, 동일한 sample space에서 여러 개의 rv가 있을 수 있음
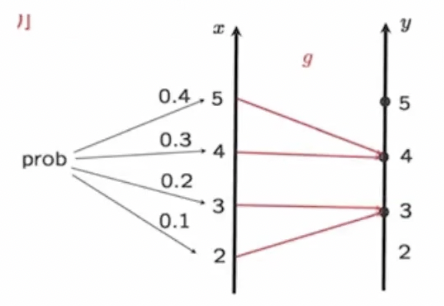
-
그렇다면 이 식은 어떠한 특성이 적용이 됨
-
-
-
Variance : measures how much the spread of a PMF is
-
동일한 expectation을 갖더라도 서로 다른 ‘형태’를 띄고 있을 수 있다.
→ 형태 : spread pattern -
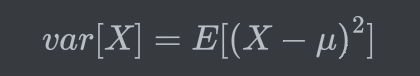
-
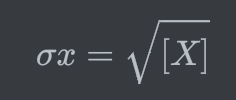
→ Standard Deviation (표준 편차) -
Variance : Useful property
-

-

→ Additional additive term does not affect to spread pattern.
-
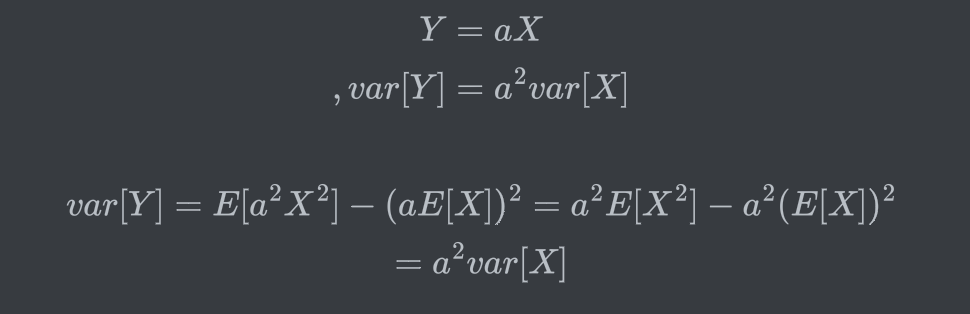
-
-
Example) Variance of a Bernoulli rv (p)
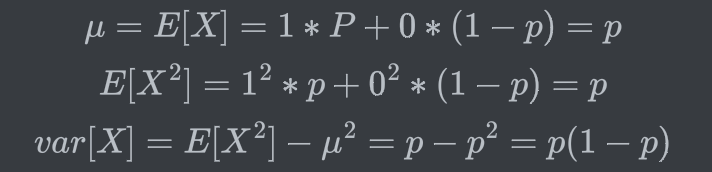
-