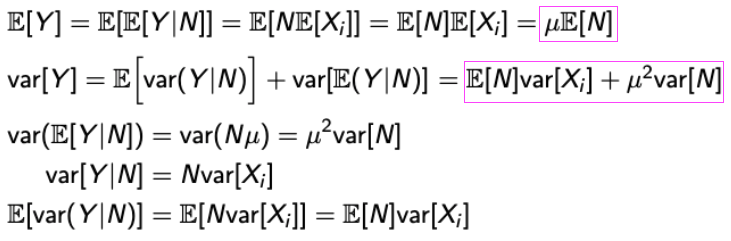Random Variables (7)
Radnom Variable (7)
현재 정리하는 내용은 KAIST EE의 이융 교수님, Probability and Intorductory Random Process 강의를 참고하여 작성했습니다.
Conditional Expectation and law of iterative expectation
A Special Random Variable
- 우리는 이전에 RV를 입력으로 받는 함수 또한 RV가 됨을 배웠다.
- 간단한 예를 통해 잠깐 보고 가자.
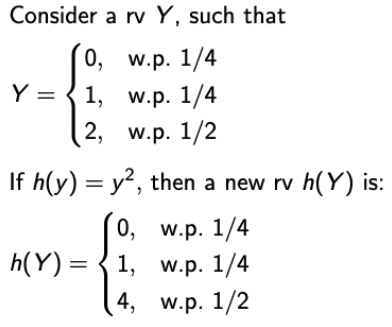
→ 먼저, Random Variable은 sample space 에서 발생하는 일을 real number로 mapping하는 함수이다.
→ 그러면, Y라는 rv가 y = 0, 1, 2로 매핑하고, 이를 h(y) = y^2을 통과시킨다면?
→ h(y)=0, 1, 4가 될 것이고, h(Y)라는 새로운 rv를 정의할 수 있다. - 이것을 살짝 바꿔서, expectation 함수를 적용해보자.
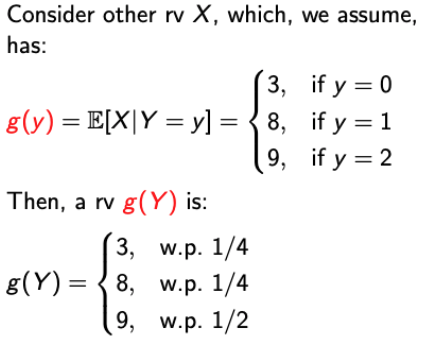
→ g(y)는 y에 의해 값이 바뀌기에 y에 대한 함수로서 정의할 수 있다.
→ 그럼 g(y)=3, 8, 9의 값으로 mapping하는 새로운 rv g(Y)를 정의할 수 있다.
→ 얘한테 fancy한 이름을 지어주자~💩
Conditional Expectation E[X | Y]
- 얘의 이름은 Conditional Expectation이다!

- 주의해야할 점이 몇가지 있다.
- Conditional Expectation is a function of Y.
- Conditional Expectation is a random variable.
- Thus, having a distribution, expectation, variance, all the things that a random variable has.
- Expectation of Conditional Expectation
- 말장난 같지만 중요한 개념이라고 한다.
- Conditional Expectation이 RV이니까 당연히 Expectation도 존재해야 한다.
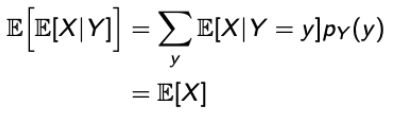
→ TET(Total Expectation Theorem)을 사용하여 증명한다.
- Examples and Meaning
- 이전에 봤던 막대 쪼개기 문제와 새로운 문제이다.

→ beg. : beginning
→ Revised forecast는 새로운 정보가 주어졌으니 E[X | Y=y]로 수정되어야 한다.
→ 이 때, 당연히 E[X | Y=y]와 E[X | Y]는 다른 값이다.
→ 하지만, law of iterated expectations 덕분에 두 개의 Expectation은 같은 값을 가지게 된다.
- Example : Averaging Quiz scores by section
- 직관적으로 지금까지 배운 Law of iterated expectation을 이해해보자.
- 한 수업에 n명의 학생이 있고, i 번째 학생의 퀴즈 점수를 xi라고 하자.

- 그런 다음에, 학생을 A1, …, Ak개의 분반으로 나누고, s 분반에 속한 학생의 수를 ns라고 해보자.
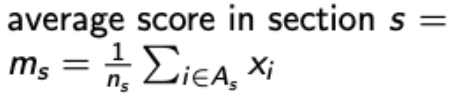
- 그러면 전체 학생의 평균을 어떻게 구할까?
- Taking the average m_s of each section
- Forming a weighted average
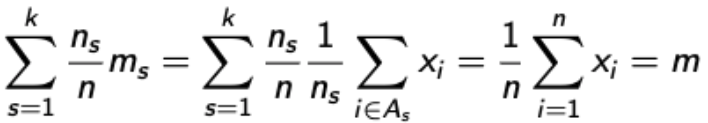
- 이거를 우리가 배운 Law of iterated expectation에 적용해보자. (TET 말고~)
- X를 랜덤하게 선택된 학생의 점수, Y는 학생의 분반이라고 해보자.
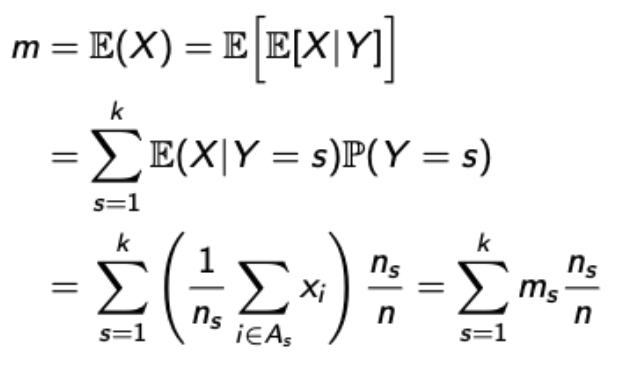
→ 💩
Conditional variance and law of total variance
Conditional Variance var[X | Y]
-
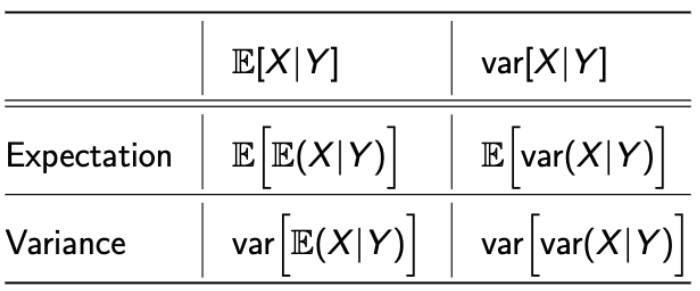
배웠던 var[X]와 이제 배울 conditional variance의 notation을 정리해보자.
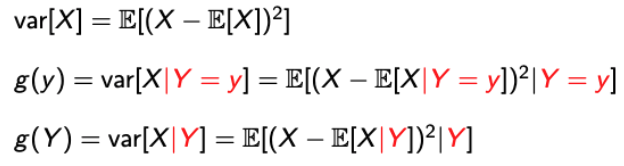
→ 앞서 배운 Conditional Expectation과 매우 유사하다. -
그럼, 똑같이 Conditional Variance의 정의를 살펴보자.

→ 물론, 이 친구도 조심해야할 점이 있다. 무엇일까? 그거다.
- Conditional Variance is a function of Y.
- Conditional Variance is a random variable.
- Thus, having a distribution, expectation, variance, all the things that a random variable has.
Expectation and Variance of E[X | Y] and var[X | Y]
- 헷갈리지만 Conditional Expectation과 Conditional Variance 둘 다 RV임을 생각한다면 이해할 수 있다.
Law of Total Variance (LTV)
-
먼저, 이 공식을 보고 그 다음에 증명을 해보자.
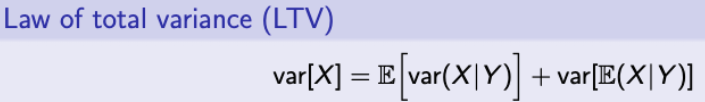
-
Proof.
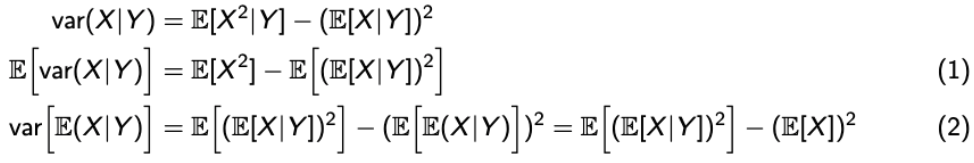
(1). 맨 위의 식에 Expectation을 적용한다면, Law of iterated expectation에 의해 식이 도출된다.
(2). E[X | Y]를 하나의 RV Z라고 생각한다면, E[Z] = E[Z^2] - (E[Z])^2이니까 쉽게 나올 수 있다. 그리고, Law of iterated expectation을 적용한다.
(1) + (2) = E[X^2] - (E[X])^2 = var[X]가 되게 된다.
- Example: Averaging Quiz Scores by Section
- LTV가 정확히 무엇을 하는지를 직관적으로 이해해보자.
- 예제는 앞서 들었던 것과 동일한 셋팅이다.
- var[X] = E[ var(X | Y) ] + var[ E(X | Y) ]라고 앞서 표현할 수 있었다.
- E[ var(X | Y) ]
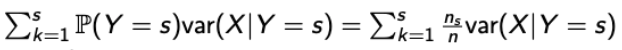
→ Weighted average of the section variances.
→ Average score variability within individual sections. → intra-variability. - var[ E(X | Y) ]
→ Variability of the average of the different sections.
→ E[X | Y = s] is average score in section s.
→ Variability between sections. → inter-variability
- E[ var(X | Y) ]
- Example: Stick-breaking
- 이것도 앞서 본 것과 같은 예제다.

Random number of sum of random variables
Sum of a random number of rvs
-
오늘 배운 Law of iterated expectation과 Law of total variance를 종합한 문제를 보자.

→ N이 고정되어 있는 숫자라면 문제는 쉬워진다.
→ E[Y] = nE[Xi]
→ Var[Y] = nVar[Xi]
→ 하지만 N은 Random이다.💩 -
그러면 공식을 적용해보자.